| .github/workflows | ||
| examples | ||
| tests | ||
| torchscale | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| README.md | ||
| SECURITY.md | ||
| setup.py | ||
| SUPPORT.md | ||
TorchScale - A Library of Foundation Architectures
TorchScale is a PyTorch library that allows researchers and developers to scale up Transformers efficiently and effectively.
Fundamental research to develop new architectures for foundation models and A(G)I, focusing on modeling generality and capability, as well as training stability and efficiency.
- Stability - DeepNet: scaling Transformers to 1,000 Layers and beyond
- Generality - Foundation Transformers (Magneto): towards true general-purpose modeling across tasks and modalities (including language, vision, speech, and multimodal)
- Capability - A Length-Extrapolatable Transformer
- Efficiency - X-MoE: scalable & finetunable sparse Mixture-of-Experts (MoE)
Revolutionizing Transformers for (M)LLMs and AI
- RetNet: Retentive Network: A Successor to Transformer for Large Language Models
- LongNet: Scaling Transformers to 1,000,000,000 Tokens
News
- October, 2023: Update RMSNorm and SwiGLU as the default module in RetNet
- November, 2022: TorchScale 0.1.1 released [Paper] [PyPI]
Installation
To install:
pip install torchscale
Alternatively, you can develop it locally:
git clone https://github.com/microsoft/torchscale.git
cd torchscale
pip install -e .
Getting Started
It takes only several lines of code to create a model with the above fundamental research features enabled. Here is how to quickly obtain a BERT-like encoder:
>>> from torchscale.architecture.config import EncoderConfig
>>> from torchscale.architecture.encoder import Encoder
>>> config = EncoderConfig(vocab_size=64000)
>>> model = Encoder(config)
>>> print(model)
We also support the Decoder architecture and the EncoderDecoder architecture:
# Creating a decoder model
>>> from torchscale.architecture.config import DecoderConfig
>>> from torchscale.architecture.decoder import Decoder
>>> config = DecoderConfig(vocab_size=64000)
>>> decoder = Decoder(config)
>>> print(decoder)
# Creating a encoder-decoder model
>>> from torchscale.architecture.config import EncoderDecoderConfig
>>> from torchscale.architecture.encoder_decoder import EncoderDecoder
>>> config = EncoderDecoderConfig(vocab_size=64000)
>>> encdec = EncoderDecoder(config)
>>> print(encdec)
It takes only several lines of code to create a RetNet model:
# Creating a RetNet model
>>> import torch
>>> from torchscale.architecture.config import RetNetConfig
>>> from torchscale.architecture.retnet import RetNetDecoder
>>> config = RetNetConfig(vocab_size=64000)
>>> retnet = RetNetDecoder(config)
>>> print(retnet)
Key Features
-
DeepNorm to improve the training stability of Post-LayerNorm Transformers
- enabled by setting deepnorm=True in the
Configclass. - It adjusts both the residual connection and the initialization method according to the model architecture (i.e., encoder, decoder, or encoder-decoder).
- enabled by setting deepnorm=True in the
-
SubLN for the model generality and the training stability
- enabled by subln=True. This is enabled by default.
- It introduces another LayerNorm to each sublayer and adjusts the initialization according to the model architecture.
- Note that SubLN and DeepNorm cannot be used in one single model.
-
X-MoE: efficient and finetunable sparse MoE modeling
- enabled by use_xmoe=True.
- It replaces every 'moe_freq'
FeedForwardNetworklayers with the X-MoE layers.
-
Multiway architecture for multimodality
- enabled by multiway=True.
- It provides a pool of Transformer's parameters used for different modalities.
-
Extrapolatable position embedding (Xpos)
- enabled by xpos_rel_pos=True.
-
- enabled by adjusting rel_pos_buckets and max_rel_pos.
-
SparseClip: improving the gradient clipping for sparse MoE models
- we provide a sample code that can be easily adapted to the FairSeq (or other) repo.
-
Retentive Network: A Successor to Transformer for Large Language Models
- created by
config = RetNetConfig(vocab_size=64000)andretnet = RetNetDecoder(config).
- created by
Most of the features above can be used by simply passing the corresponding parameters to the config. For example:
>>> from torchscale.architecture.config import EncoderConfig
>>> from torchscale.architecture.encoder import Encoder
>>> config = EncoderConfig(vocab_size=64000, deepnorm=True, multiway=True)
>>> model = Encoder(config)
>>> print(model)
Examples
We have examples of how to use TorchScale in the following scenarios/tasks:
-
Language
-
Vision
- ViT/BEiT [In progress]
-
Speech
-
Multimodal
We plan to provide more examples regarding different tasks (e.g. vision pretraining and speech recognition) and various deep learning toolkits (e.g. DeepSpeed and Megatron-LM). Any comments or PRs are welcome!
Results
Stability Evaluation
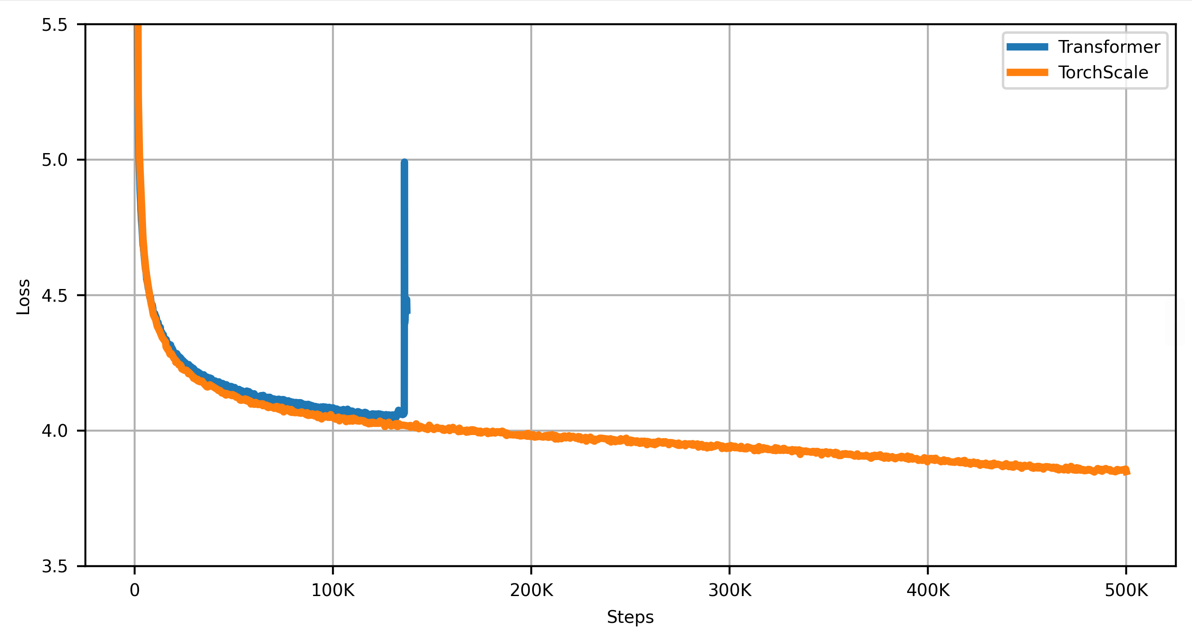
The training curve is smooth by using TorchScale, while the baseline Transformer cannot converge.
Scaling-up Experiments
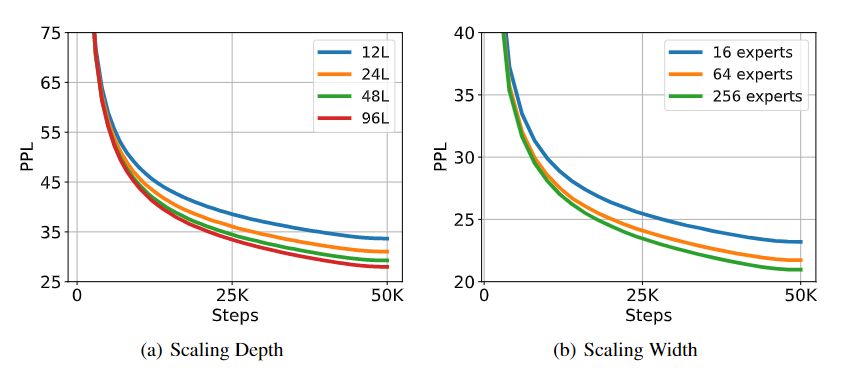
TorchScale supports arbitrary depths and widths, successfully scaling-up the models without pain.
Acknowledgments
Some implementations in TorchScale are either adapted from or inspired by the FairSeq repository and the UniLM repository.
Citations
If you find this repository useful, please consider citing our work:
@article{torchscale,
author = {Shuming Ma and Hongyu Wang and Shaohan Huang and Wenhui Wang and Zewen Chi and Li Dong and Alon Benhaim and Barun Patra and Vishrav Chaudhary and Xia Song and Furu Wei},
title = {{TorchScale}: {Transformers} at Scale},
journal = {CoRR},
volume = {abs/2211.13184},
year = {2022}
}
@article{deepnet,
author = {Hongyu Wang and Shuming Ma and Li Dong and Shaohan Huang and Dongdong Zhang and Furu Wei},
title = {{DeepNet}: Scaling {Transformers} to 1,000 Layers},
journal = {CoRR},
volume = {abs/2203.00555},
year = {2022},
}
@article{magneto,
author = {Hongyu Wang and Shuming Ma and Shaohan Huang and Li Dong and Wenhui Wang and Zhiliang Peng and Yu Wu and Payal Bajaj and Saksham Singhal and Alon Benhaim and Barun Patra and Zhun Liu and Vishrav Chaudhary and Xia Song and Furu Wei},
title = {Foundation {Transformers}},
journal = {CoRR},
volume = {abs/2210.06423},
year = {2022}
}
@inproceedings{xmoe,
title={On the Representation Collapse of Sparse Mixture of Experts},
author={Zewen Chi and Li Dong and Shaohan Huang and Damai Dai and Shuming Ma and Barun Patra and Saksham Singhal and Payal Bajaj and Xia Song and Xian-Ling Mao and Heyan Huang and Furu Wei},
booktitle={Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems},
year={2022},
url={https://openreview.net/forum?id=mWaYC6CZf5}
}
@article{retnet,
author={Yutao Sun and Li Dong and Shaohan Huang and Shuming Ma and Yuqing Xia and Jilong Xue and Jianyong Wang and Furu Wei},
title = {Retentive Network: A Successor to {Transformer} for Large Language Models},
journal = {ArXiv},
volume = {abs/2307.08621},
year = {2023}
}
Contributing
This project welcomes contributions and suggestions. Most contributions require you to agree to a Contributor License Agreement (CLA) declaring that you have the right to, and actually do, grant us the rights to use your contribution. For details, visit https://cla.opensource.microsoft.com.
When you submit a pull request, a CLA bot will automatically determine whether you need to provide a CLA and decorate the PR appropriately (e.g., status check, comment). Simply follow the instructions provided by the bot. You will only need to do this once across all repos using our CLA.
This project has adopted the Microsoft Open Source Code of Conduct. For more information, see the Code of Conduct FAQ or contact Furu Wei and Shuming Ma with any additional questions or comments.
Trademarks
This project may contain trademarks or logos for projects, products, or services. Authorized use of Microsoft trademarks or logos is subject to and must follow Microsoft's Trademark & Brand Guidelines. Use of Microsoft trademarks or logos in modified versions of this project must not cause confusion or imply Microsoft sponsorship. Any use of third-party trademarks or logos is subject to those third-party's policies.
